How to fix manganese deficiency in cannabis

Manganese deficiency in cannabis plants can feel like a daunting challenge, but don’t worry – it’s completely fixable. This guide will help you understand what manganese does for your plants, how to spot deficiencies, and the best ways to treat and prevent the problem. Let’s dive in and get your plants thriving again!
Understanding manganese deficiency in cannabis
Manganese plays a crucial role in the health of cannabis plants. It’s a micronutrient, meaning your plants need it in small amounts, but its impact is massive. Manganese is key for photosynthesis and enzyme activation, which are the backbone of healthy growth.
Role of manganese in cannabis plant health
Manganese is essential for chloroplast formation and photosynthesis. It helps your plants convert sunlight into the energy they need to grow. It also plays a part in nitrogen assimilation, which is crucial for strong, vibrant foliage.
Causes of manganese deficiency in cannabis plants
The main culprit behind manganese deficiency is usually a pH imbalance. When the soil or nutrient solution’s pH is too high, manganese becomes unavailable to your plants. Overwatering, nutrient lockout, or poor-quality soil can also contribute.
Identifying symptoms of manganese deficiency
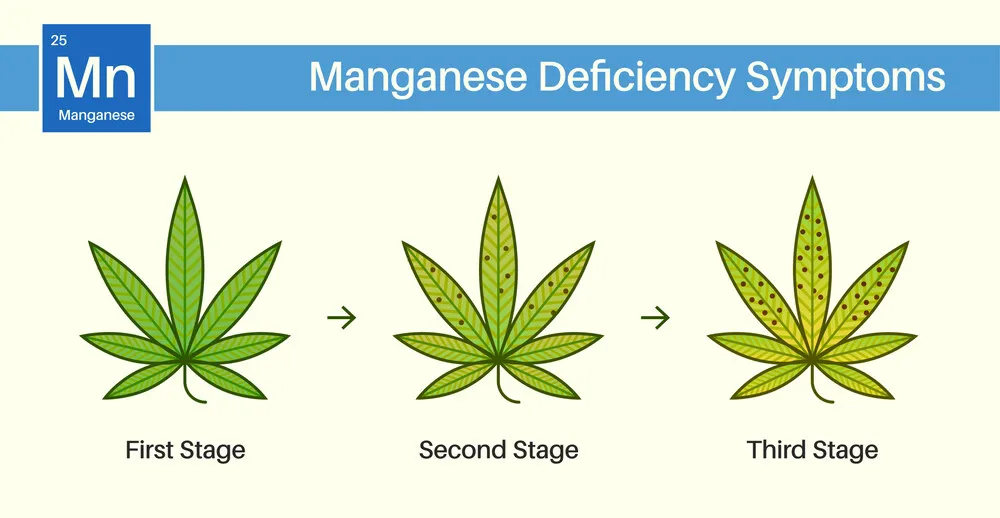
Spotting manganese deficiency early can save your plants from long-term damage. Keep an eye on your leaves for signs of trouble.
Early signs: interveinal chlorosis and leaf discoloration
Early on, you’ll notice interveinal chlorosis – where the spaces between the veins of the leaves turn yellow while the veins remain green. This usually starts on younger leaves.
Advanced symptoms: necrotic spots and stunted growth
If untreated, yellow patches can develop into brown necrotic spots. The plant’s overall growth may slow, and leaves may appear brittle or distorted.
Diagnosing manganese deficiency accurately
It’s important to confirm manganese deficiency before jumping to treatments. Misdiagnosing can lead to unnecessary corrections that stress your plants further.
Differentiating from other nutrient deficiencies
Manganese deficiency is often confused with iron or magnesium deficiencies because they also cause yellowing leaves. The key difference is that manganese deficiency usually affects new growth first, while iron and magnesium deficiencies show up on older leaves.
Importance of monitoring soil pH levels
Testing your soil or nutrient solution’s pH is crucial. Manganese is most available when the pH is between 5.5 and 6.5. Adjusting pH into this range can often resolve the issue without additional supplements.
Effective treatment strategies for manganese deficiency
Once you’ve identified manganese deficiency, it’s time to take action. Here’s how to nurse your plants back to health.
Adjusting soil pH to enhance manganese uptake

If the pH is too high, lower it using pH-adjusting solutions. For soil, you can use sulfur or organic matter like peat moss. In hydroponics, pH-down solutions work best. Keep testing until you hit the sweet spot.
Implementing foliar feeding with manganese supplements
Foliar feeding is a quick fix. Mix a manganese supplement with water and spray it directly onto your plants’ leaves. This delivers manganese straight to where it’s needed.
Ensuring proper watering practices to prevent nutrient lockout
Overwatering can flush essential nutrients out of the soil. Water your plants only when the top inch of soil feels dry. This also helps prevent root rot and other stressors.
Preventing future manganese deficiencies
Prevention is always better than cure. With a few simple steps, you can stop manganese deficiency before it starts.
Regular soil testing and pH monitoring
Check your soil’s pH regularly. Investing in a good pH meter can save you a lot of headaches down the line. Adjusting pH proactively keeps your plants happy and healthy.
Balanced fertilization and micronutrient management
Use a balanced fertilizer that includes micronutrients. Products labeled for cannabis or general hydroponics often have the right mix. Follow feeding schedules and avoid over-fertilizing, which can lead to lockout.
FAQs:
What are the first signs of manganese deficiency in cannabis plants?
The first signs are yellowing between the veins (interveinal chlorosis) on new leaves. These symptoms indicate that the plant isn’t getting enough manganese, often due to pH imbalance or nutrient lockout.
How does soil pH affect manganese availability to cannabis plants?
Manganese is most available at a pH of 5.5 to 6.5. Outside this range, manganese binds to the soil and becomes unavailable, leading to deficiency symptoms.
Can manganese deficiency be mistaken for other nutrient deficiencies?
Yes, it’s often confused with magnesium or iron deficiencies. The key difference is that manganese deficiency affects new growth, while the others target older leaves.
What are the best methods to treat manganese deficiency in hydroponic cannabis systems?
Adjust the nutrient solution’s pH to 5.5-6.0 and add a manganese supplement. Foliar feeding can also provide a quick fix while the root zone recovers.
How can I prevent manganese deficiency during different cannabis growth stages?
Monitor pH levels regularly, use a balanced fertilizer, and avoid overwatering. Ensuring proper micronutrient levels throughout all growth stages will keep your plants thriving.
By following this guide, you’ll not only fix manganese deficiency in your cannabis plants but also set them up for long-term success. Healthy plants lead to better yields, so keep nurturing them with care!
-
20+ Years Experience
Over 500K seeds sold worldwide
100K+ Happy Customers -
Germination Guaranteed
Complete satisfaction or we will replace your order -
Dutch and USA Genetics
Master breeders inspiring strains from across the world -
1-5 Day Delivery - Guaranteed
Free Express Shipping to the US, Canada and UK








